Circular Queue in Data Structure and Algorithm
A circular queue is similar to a linear queue as it is also based on the FIFO principle except that the last position is connected to the first position in circular queue that forms a circle. so it is also known as a Ring buffer.
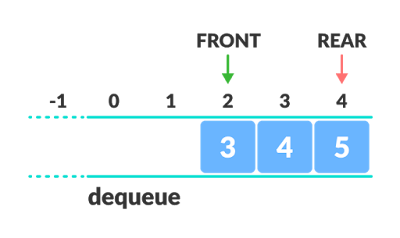
Circular queue Representation :
The circular queue solves the major limitation of the normal queue. In a normal queue, after a bit of insertion and deletion, there will be non-usable empty space.
How Circular Queue Works :
Circular Queue works by the process of circular increment i.e. when we try to increment the pointer and we reach the end of the queue, we start from the beginning of the queue.
Here, the circular increment is performed by modulo division with the queue size. That is,
if REAR + 1 == 5 (overflow!), REAR = (REAR + 1)%5 = 0 (start of queue)
Circular Queue Operations :
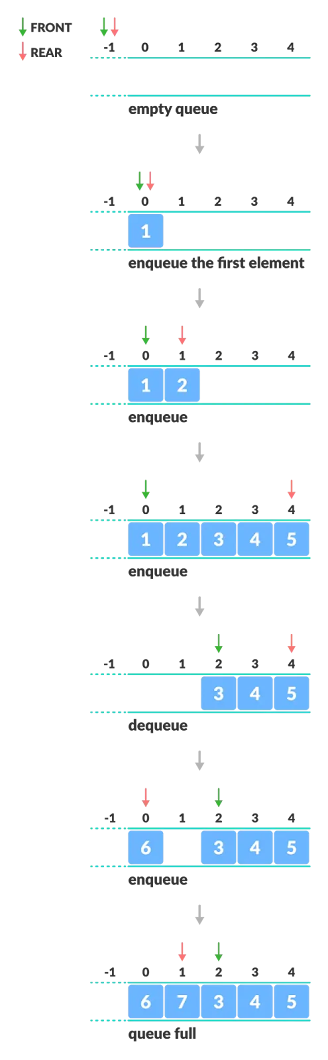
The circular queue work as follows:
- two pointers FRONT and REAR
- FRONT track the first element of the queue
- REAR track the last elements of the queue
- initially, set value of FRONT and REAR to -1
1. Enqueue Operation
- check if the queue is full
- for the first element, set value of FRONT to 0
- circularly increase the REAR index by 1 (i.e. if the rear reaches the end, next it would be at the start of the queue)
- add the new element in the position pointed to by REAR
2. Dequeue Operation
- check if the queue is empty
- return the value pointed by FRONT
- circularly increase the FRONT index by 1
- for the last element, reset the values of FRONT and REAR to -1
However, the check for full queue has a new additional case:
- Case 1: FRONT = 0 && REAR == SIZE - 1
- Case 2: FRONT = REAR + 1
The second case happens when REAR starts from 0 due to circular increment and when its value is just 1 less than FRONT, the queue is full.
Circular Queue Implementation :
// Circular Queue implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 5
int items[SIZE];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
// Check if the queue is full
int isFull() {
if ((front == rear + 1) || (front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1)) return 1;
return 0;
}
// Check if the queue is empty
int isEmpty() {
if (front == -1) return 1;
return 0;
}
// Adding an element
void enQueue(int element) {
if (isFull())
printf("\n Queue is full!! \n");
else {
if (front == -1) front = 0;
rear = (rear + 1) % SIZE;
items[rear] = element;
printf("\n Inserted -> %d", element);
}
}
// Removing an element
int deQueue() {
int element;
if (isEmpty()) {
printf("\n Queue is empty !! \n");
return (-1);
} else {
element = items[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Q has only one element, so we reset the
// queue after dequeing it. ?
else {
front = (front + 1) % SIZE;
}
printf("\n Deleted element -> %d \n", element);
return (element);
}
}
// Display the queue
void display() {
int i;
if (isEmpty())
printf(" \n Empty Queue\n");
else {
printf("\n Front -> %d ", front);
printf("\n Items -> ");
for (i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % SIZE) {
printf("%d ", items[i]);
}
printf("%d ", items[i]);
printf("\n Rear -> %d \n", rear);
}
}
int main() {
// Fails because front = -1
deQueue();
enQueue(1);
enQueue(2);
enQueue(3);
enQueue(4);
enQueue(5);
// Fails to enqueue because front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1
enQueue(6);
display();
deQueue();
display();
enQueue(7);
display();
// Fails to enqueue because front == rear + 1
enQueue(8);
return 0;
}
Implementation in C++ :
// Circular Queue implementation in C++
#include <iostream>
#define SIZE 5 /* Size of Circular Queue */
using namespace std;
class Queue {
private:
int items[SIZE], front, rear;
public:
Queue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Check if the queue is full
bool isFull() {
if (front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1) {
return true;
}
if (front == rear + 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Check if the queue is empty
bool isEmpty() {
if (front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Adding an element
void enQueue(int element) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue is full";
} else {
if (front == -1) front = 0;
rear = (rear + 1) % SIZE;
items[rear] = element;
cout << endl
<< "Inserted " << element << endl;
}
}
// Removing an element
int deQueue() {
int element;
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty" << endl;
return (-1);
} else {
element = items[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Q has only one element,
// so we reset the queue after deleting it.
else {
front = (front + 1) % SIZE;
}
return (element);
}
}
void display() {
// Function to display status of Circular Queue
int i;
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << endl
<< "Empty Queue" << endl;
} else {
cout << "Front -> " << front;
cout << endl
<< "Items -> ";
for (i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % SIZE)
cout << items[i];
cout << items[i];
cout << endl
<< "Rear -> " << rear;
}
}
};
int main() {
Queue q;
// Fails because front = -1
q.deQueue();
q.enQueue(1);
q.enQueue(2);
q.enQueue(3);
q.enQueue(4);
q.enQueue(5);
// Fails to enqueue because front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1
q.enQueue(6);
q.display();
int elem = q.deQueue();
if (elem != -1)
cout << endl
<< "Deleted Element is " << elem;
q.display();
q.enQueue(7);
q.display();
// Fails to enqueue because front == rear + 1
q.enQueue(8);
return 0;
}
Implementation in JAVA :
// Circular Queue implementation in Java
public class CQueue {
int SIZE = 5; // Size of Circular Queue
int front, rear;
int items[] = new int[SIZE];
CQueue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Check if the queue is full
boolean isFull() {
if (front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1) {
return true;
}
if (front == rear + 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Check if the queue is empty
boolean isEmpty() {
if (front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Adding an element
void enQueue(int element) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is full");
} else {
if (front == -1)
front = 0;
rear = (rear + 1) % SIZE;
items[rear] = element;
System.out.println("Inserted " + element);
}
}
// Removing an element
int deQueue() {
int element;
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return (-1);
} else {
element = items[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
} /* Q has only one element, so we reset the queue after deleting it. */
else {
front = (front + 1) % SIZE;
}
return (element);
}
}
void display() {
/* Function to display status of Circular Queue */
int i;
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Empty Queue");
} else {
System.out.println("Front -> " + front);
System.out.println("Items -> ");
for (i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % SIZE)
System.out.print(items[i] + " ");
System.out.println(items[i]);
System.out.println("Rear -> " + rear);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CQueue q = new CQueue();
// Fails because front = -1
q.deQueue();
q.enQueue(1);
q.enQueue(2);
q.enQueue(3);
q.enQueue(4);
q.enQueue(5);
// Fails to enqueue because front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1
q.enQueue(6);
q.display();
int elem = q.deQueue();
if (elem != -1) {
System.out.println("Deleted Element is " + elem);
}
q.display();
q.enQueue(7);
q.display();
// Fails to enqueue because front == rear + 1
q.enQueue(8);
}
}
Implementation in Python :
# Circular Queue implementation in Python
class MyCircularQueue():
def __init__(self, k):
self.k = k
self.queue = [None] * k
self.head = self.tail = -1
# Insert an element into the circular queue
def enqueue(self, data):
if ((self.tail + 1) % self.k == self.head):
print("The circular queue is full\n")
elif (self.head == -1):
self.head = 0
self.tail = 0
self.queue[self.tail] = data
else:
self.tail = (self.tail + 1) % self.k
self.queue[self.tail] = data
# Delete an element from the circular queue
def dequeue(self):
if (self.head == -1):
print("The circular queue is empty\n")
elif (self.head == self.tail):
temp = self.queue[self.head]
self.head = -1
self.tail = -1
return temp
else:
temp = self.queue[self.head]
self.head = (self.head + 1) % self.k
return temp
def printCQueue(self):
if(self.head == -1):
print("No element in the circular queue")
elif (self.tail >= self.head):
for i in range(self.head, self.tail + 1):
print(self.queue[i], end=" ")
print()
else:
for i in range(self.head, self.k):
print(self.queue[i], end=" ")
for i in range(0, self.tail + 1):
print(self.queue[i], end=" ")
print()
# Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
obj = MyCircularQueue(5)
obj.enqueue(1)
obj.enqueue(2)
obj.enqueue(3)
obj.enqueue(4)
obj.enqueue(5)
print("Initial queue")
obj.printCQueue()
obj.dequeue()
print("After removing an element from the queue")
obj.printCQueue()
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now