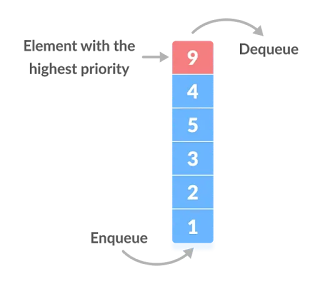
A priority queue is a special type of queue in which each element is associated with a priority value. And, elements are served on the basis of their priority. That is, higher priority elements are served first.
However, if elements with the same priority occur, they are served according to their order in the queue.
Assigning Priority Value
Generally, the value of the element itself is considered for assigning the priority. For example,
The element with the highest value is considered the highest priority element. However, in other cases, we can assume the element with the lowest value as the highest priority element.
We can also set priorities according to our needs.
If there is no node, create a newNode. else (a node is already present) insert the newNode at the end (last node from left to right.) heapify the array
For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that parentNode is always smaller than newNode.
2. Deleting an Element from the Priority Queue
Deleting an element from a priority queue (max-heap) is done as follows:
Select the element to be deleted.
If nodeToBeDeleted is the leafNode remove the node Else swap nodeToBeDeleted with the lastLeafNode remove noteToBeDeleted heapify the array
For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that the both childNodes are smaller than currentNode.
3. Peeking from the Priority Queue (Find max/min)
Peek operation returns the maximum element from Max Heap or minimum element from Min Heap without deleting the node.
For both Max heap and Min Heap
return rootNode
4. Extract-Max/Min from the Priority Queue
Extract-Max returns the node with maximum value after removing it from a Max Heap whereas Extract-Min returns the node with minimum value after removing it from Min Heap.
Priority Queue Implementations in C and Java :
Code in C :
// Priority Queue implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
int size = 0;
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(int array[], int size, int i) {
if (size == 1) {
printf("Single element in the heap");
} else {
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && array[l] > array[largest])
largest = l;
if (r < size && array[r] > array[largest])
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(&array[i], &array[largest]);
heapify(array, size, largest);
}
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(int array[], int newNum) {
if (size == 0) {
array[0] = newNum;
size += 1;
} else {
array[size] = newNum;
size += 1;
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(array, size, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteRoot(int array[], int num) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == array[i])
break;
}
swap(&array[i], &array[size - 1]);
size -= 1;
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(array, size, i);
}
}
// Print the array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
printf("%d ", array[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[10];
insert(array, 3);
insert(array, 4);
insert(array, 9);
insert(array, 5);
insert(array, 2);
printf("Max-Heap array: ");
printArray(array, size);
deleteRoot(array, 4);
printf("After deleting an element: ");
printArray(array, size);
}
Code in Java :
// Priority Queue implementation in Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Heap {
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int i) {
int size = hT.size();
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && hT.get(l) > hT.get(largest))
largest = l;
if (r < size && hT.get(r) > hT.get(largest))
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
int temp = hT.get(largest);
hT.set(largest, hT.get(i));
hT.set(i, temp);
heapify(hT, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int newNum) {
int size = hT.size();
if (size == 0) {
hT.add(newNum);
} else {
hT.add(newNum);
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteNode(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int num) {
int size = hT.size();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == hT.get(i))
break;
}
int temp = hT.get(i);
hT.set(i, hT.get(size - 1));
hT.set(size - 1, temp);
hT.remove(size - 1);
for (int j = size / 2 - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
heapify(hT, j);
}
}
// Print the tree
void printArray(ArrayList<Integer> array, int size) {
for (Integer i : array) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = array.size();
Heap h = new Heap();
h.insert(array, 3);
h.insert(array, 4);
h.insert(array, 9);
h.insert(array, 5);
h.insert(array, 2);
System.out.println("Max-Heap array: ");
h.printArray(array, size);
h.deleteNode(array, 4);
System.out.println("After deleting an element: ");
h.printArray(array, size);
}
}
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now